What Are the Different Types of Head Injuries?

Samson Zain . Follow
7 months ago
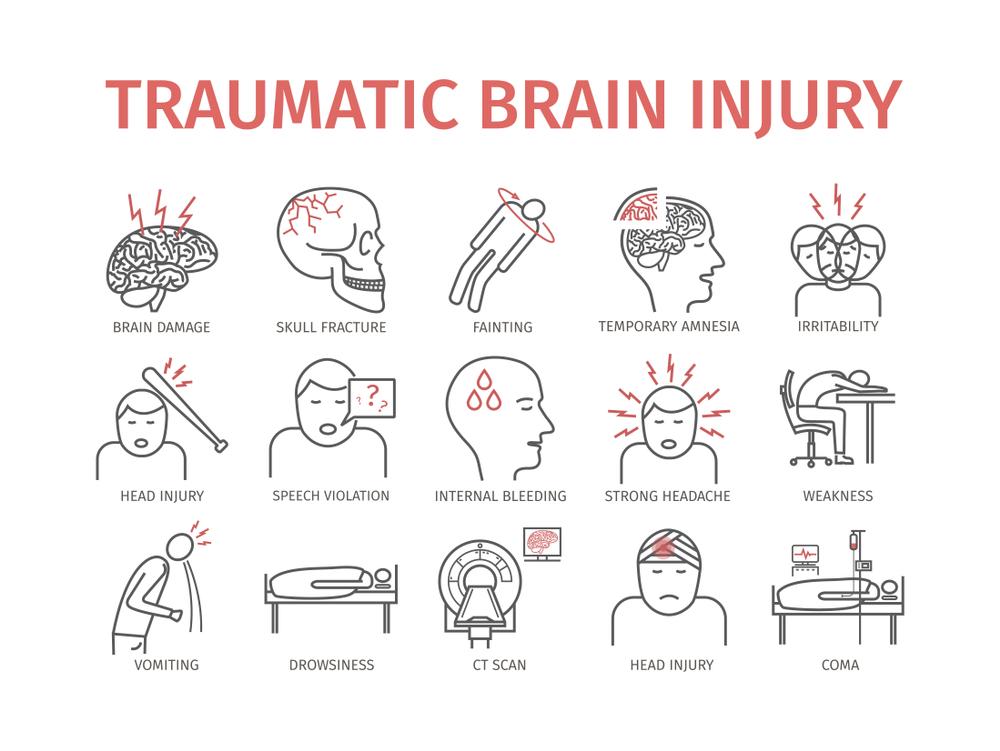
Head injuries can range from mild concussions to severe traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), and they can have significant short- and long-term consequences. Understanding the various types of head injuries is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of head injuries, their causes, symptoms, and potential treatments, with a particular focus on cerebrolysin injection as a therapeutic intervention.
1. Concussion
Concussions are among the most common types of head injuries and are often caused by a blow to the head or sudden acceleration or deceleration of the brain within the skull. Symptoms of a concussion can include headache, confusion, dizziness, nausea, and sensitivity to light or noise.
While most concussions resolve on their own with rest and symptom management, severe cases may require medical intervention. The cerebrolysin injection, a neurotrophic medication derived from pig brain tissue, has shown promise in accelerating recovery and reducing symptoms associated with concussions by promoting neuronal growth and repair.
2. Contusion
A contusion refers to bruising of the brain tissue, typically caused by a direct impact to the head. Symptoms of a cerebral contusion can vary depending on the severity and location of the injury but may include headache, dizziness, memory loss, and altered consciousness.
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove blood clots or relieve pressure on the brain. Cerebrolysin injection has been investigated as a potential adjunctive treatment for cerebral contusions, with studies suggesting its ability to enhance neuroplasticity and improve functional outcomes.
3. Skull Fracture
A skull fracture occurs when there is a break in the bone surrounding the brain. This type of head injury can result from significant force or trauma to the head, such as a fall or motor vehicle accident. Symptoms of a skull fracture may include pain at the site of the injury, swelling, bruising, and in severe cases, visible deformity or depression of the skull.
While minor fractures may heal on their own with rest and pain management, more serious fractures may require surgical intervention to repair the damage. Cerebrolysin injection has been explored as a potential treatment for skull fractures due to its neuroprotective properties and ability to enhance the brain's regenerative processes.
4. Hematoma
A hematoma is a collection of blood outside of blood vessels, typically within the brain tissue or between the brain and the skull. There are several types of hematomas, including epidural, subdural, and intracerebral hematomas, each with its own causes and symptoms.
Symptoms of a hematoma may include headache, vomiting, confusion, weakness, and seizures. Treatment for a hematoma depends on the type and severity of the injury but may involve surgical evacuation of the blood clot. Cerebrolysin injection has been investigated as a potential adjunctive therapy for hematomas, with studies suggesting its ability to reduce inflammation, promote tissue repair, and improve neurological outcomes.
5. Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI)
Diffuse axonal injury is a severe form of head injury characterized by widespread damage to the brain's white matter tracts. DAI often results from high-speed acceleration-deceleration forces, such as those seen in motor vehicle accidents or shaken baby syndrome.
Symptoms of DAI can vary widely and may include unconsciousness, coma, cognitive impairment, and motor deficits. Treatment for DAI is challenging, and the focus is typically on supportive care and rehabilitation to minimize long-term disability. While cerebrolysin injection has not been specifically studied in the treatment of DAI, its neurotrophic properties may offer potential benefits in promoting axonal repair and functional recovery.
Conclusion
Head injuries encompass a broad spectrum of conditions, ranging from mild concussions to severe traumatic brain injuries. Prompt recognition and appropriate management of these injuries are essential to minimize complications and optimize outcomes for affected individuals.
While conventional treatments focus on supportive care, surgery, and rehabilitation, emerging therapies such as cerebrolysin injection hold promise for enhancing neuronal repair and improving functional recovery. Further research is needed to elucidate the role of cerebrolysin and other neurotrophic agents in the treatment of various types of head injuries and to refine treatment protocols for optimal patient outcomes.


